Pedestrian Level Of Service (PLOS) is being increasingly used to assess safety and comfort levels across entire cities, providing effective indications on priority of interventions.
With the increase of car-dependence, design of streets is becoming more and more a matter that exclusively regards motorized vehicles, while little attention to design adequate spaces and facilities for pedestrian movements. Consequently, people usually use cars for walkable trips, a decision predominantly influenced by the lack of services and venues at ground levels as well as inadequate sidewalk design. Therefore, to encourage walking as a viable mode of transport for short trips, it is necessary to set higher design standards of the urban realm hence creating better walking conditions and an enhanced pedestrian experience.
To objectively measure and evaluate the current walking conditions, developing a tool for Pedestrian Level of Service is necessary. The Pedestrian Level of Service (PLOS) is a complex measure, which permits to quantify comfort and safety levels of existing and planned walkways allowing objective and sound evaluations of pedestrians’ perception and response to roadway environment.
With the scope to develop the Pedestrian Level of Service in Dubai, a detailed GIS model is developed to incorporate the entire range of necessary attributes, quantitative and qualitative, of streets and sidewalks. The input variables considered in the Pedestrian Level of Service analysis reflect different characteristics of roads. The first is the motorized traffic, for which vehicular traffic volumes, vehicle speed and the percentage of occupied parking are taken into consideration. The second is the roadway, for which the number of street lanes and the presence of median in roads are taken into consideration. The last one is the sidewalk, for which several variables, such as the width of the sidewalk, the width of the buffer between sidewalk and roadway, the presence of greenery within the buffer area and the presence of bike lanes are taken into consideration.
The computation of these variables allows to categorize the roads of Dubai in six Pedestrian Level of Service classes, defined according to the quality of the street, from best to worst conditions:
● plos a: Streets with higher level of service are characterized by a highly pedestrian-oriented environment, with ample sidewalks and a green buffer space between road and sidewalk.
● plos b: These streets, similar to the previous rank, have low vehicular traffic volumes and many pedestrian safety and comfort features implemented.
● plos c: Streets with standard-size sidewalks, but with some deficiencies in pedestrian facility design or higher vehicular traffic volumes.
● plos d: Streets are adequate for pedestrian use but the frequent deficiencies in the width of sidewalks and safety of pedestrians decreases the walking conditions on these streets.
● plos e: These streets are inadequate for pedestrian use, since they have high levels of interaction with traffic and very little space dedicated to pedestrians.
● plos f: Streets with the lower level of service are characterized by an extremely car-oriented environment, where roads are designed for high vehicular traffic volumes and sidewalks are usually not present.
In conclusion, the Pedestrian Level of Service is a mathematical method, which permits to evaluate the comfort and safety level of pedestrian experience within a roadway environment, defining an output that can be integrated with planning decisions, prioritizing the needs of existing streets for sidewalk retrofit.
Elements increasing the Pedestrian Level of Service
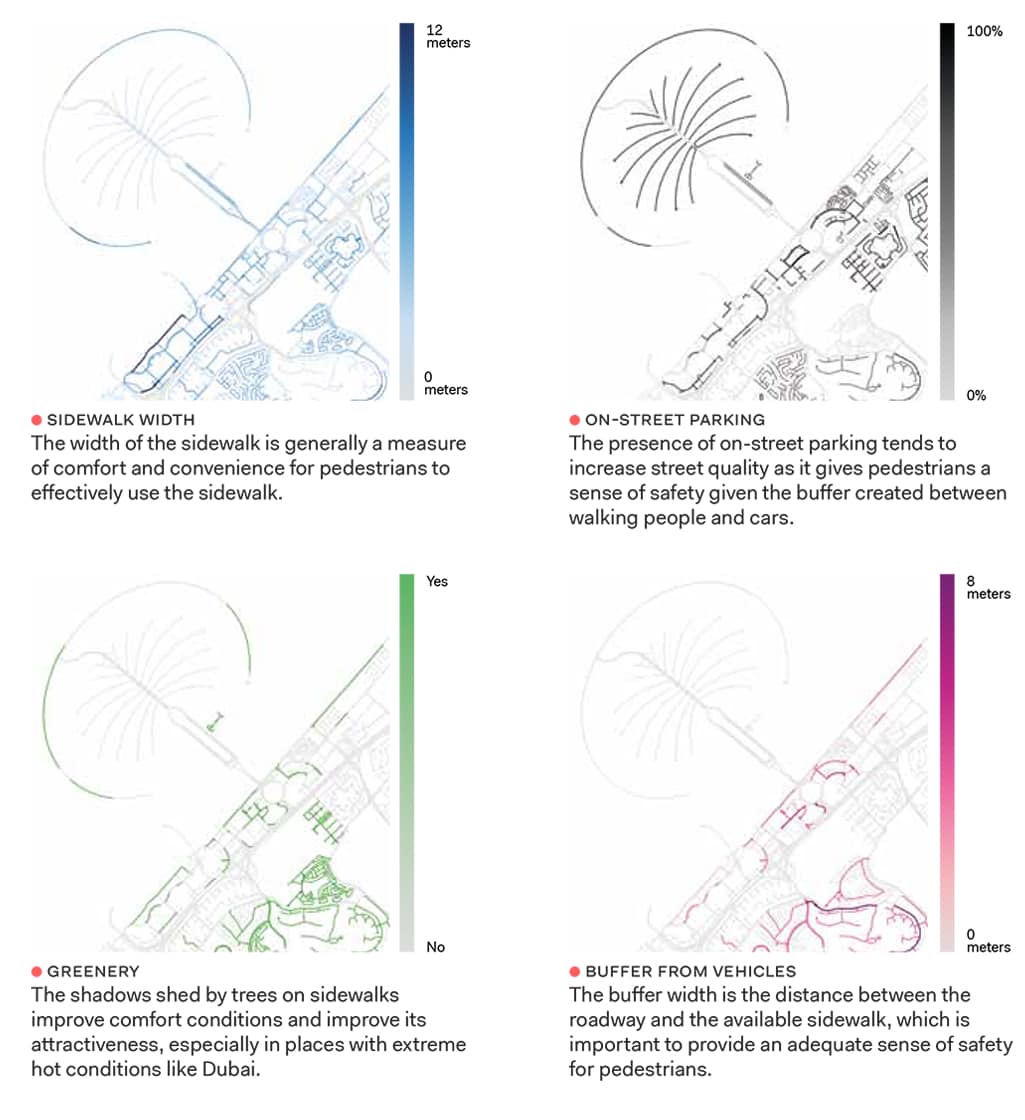
Among the quantitative and qualitative measures influencing the Pedestrian Level of Service, there are four elements, which increase the score: sidewalk width, on-street parking, greenery and buffer from vehicles.
Elements decreasing the Pedestrian Level of Service
Among the quantitative and qualitative measures affecting the Pedestrian Level of Service, there are four elements, which decrease the score: vehicle speed, number of lanes, vehicular traffic and the presence of the median.